Setup & Running
In order to get status-checks setup and running you will need to:
Setup a GitHub API token
status-checks needs an GitHub API token in order to read and write to your repository.
The application makes requests to create and edit status checks, and you might also want to do other things with the octokit api that is exposed to you (more about this later).
To setup your API token you can read and follow the documentation from GitHub or follow the steps listed below.
Creating a API Token
Steps
- Login to GitHub and go to your Settings.
- Click on
Developer Settingson the settings menu. Personal Access Tokenson the Developer Settings menu.- Click
Generate new tokento create a new token for this application. (insert something useful to name the token for example:status-check-app)
Next select the scopes for the token (as seen in the picture below).
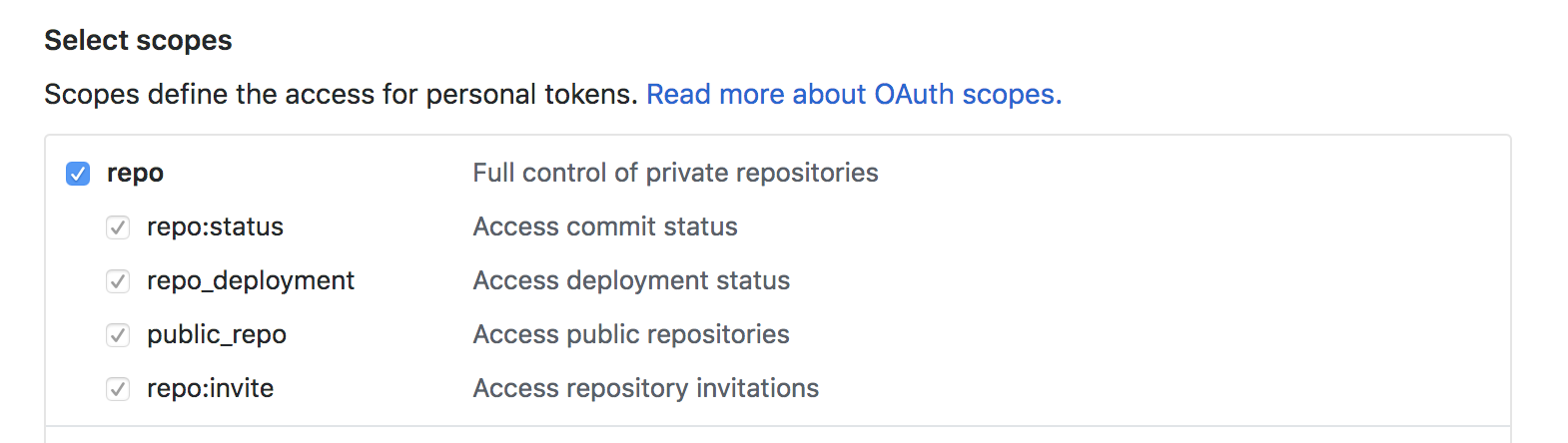
Once you have selected them, click Generate token.
This will show you a screen with your GitHub token. Copy this value.
Remember, never let anybody get access to your Tokens and never commit them back into the project.
Adding your API token
If you have the project cloned on your machine open the project and edit the .env-example file.
First rename the file to .env (this is used to store your environment variables). Inside the file you should see:
GITHUB_TOKEN=
GITHUB_SECRET=
Set the GITHUB_TOKEN value to your new GitHub API token.
Example
GITHUB_TOKEN=MY_GITHUB_TOKEN
GITHUB_SECRET=
That's it!
Now the final part, lets setup the webhook so GitHub can trigger the status checks.
Setting up the webhook
We need to integrate GitHub with your functions.
The GitHub webhook will trigger status-checks app to run your functions.
To setup the webhook you can follow the official documentation or follow the steps below.
Creating a webhook
Webhooks require you to have your application running somewhere so GitHub can start to POST data to it.
You have two options:
- Host the application yourself
- Running the application locally
We will focus on running locally for now.
If you want to host this application that is fine. This guide will not explain how to host the application, you do host it using various platforms (AWS, Now.sh, etc.). Once you have your application hosted you will need to change the webhook url to point to your hosted url.
Setup webhook with local running project
If you haven't already go clone the repository.
Next go into the project and run:
npm install && npm start
This will start the application and it will be running on http://localhost:3000.
Great, next we have to expose this endpoint so GitHub can talk to it.
Exposing Localhost for GitHub
To expose a local endpoint you have a couple of options:
We will use ngrok in this example.
With your application still running, open up another terminal and run:
npx ngrok http 3000
Ngrok will setup a tunnel to your machine running on port 3000. This is great for development and will allow GitHub to talk to your application.
Once you run ngrok you should see something like this:
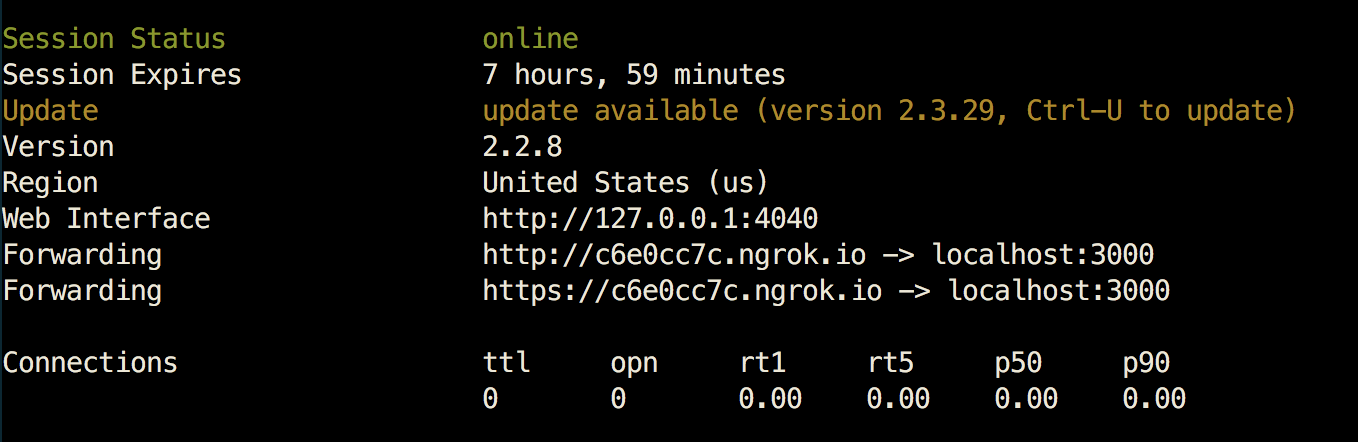
Take one of the Forwarding urls and copy it.
Next we have to setup GitHub.
Configure GitHub to use the webhook
Go to the GitHub project you want to integrate status-checks with and go to the project settings.
Click on Webhooks in the side menu and then click on Add webhook
You will be shown a new page to setup your webhook.
You will need to:
- Add the ngrok url
- Add a secret (you need this in your
.envfile) - Set the
Content Typetoapplication/json - Set
Send me everything
Here is an example:
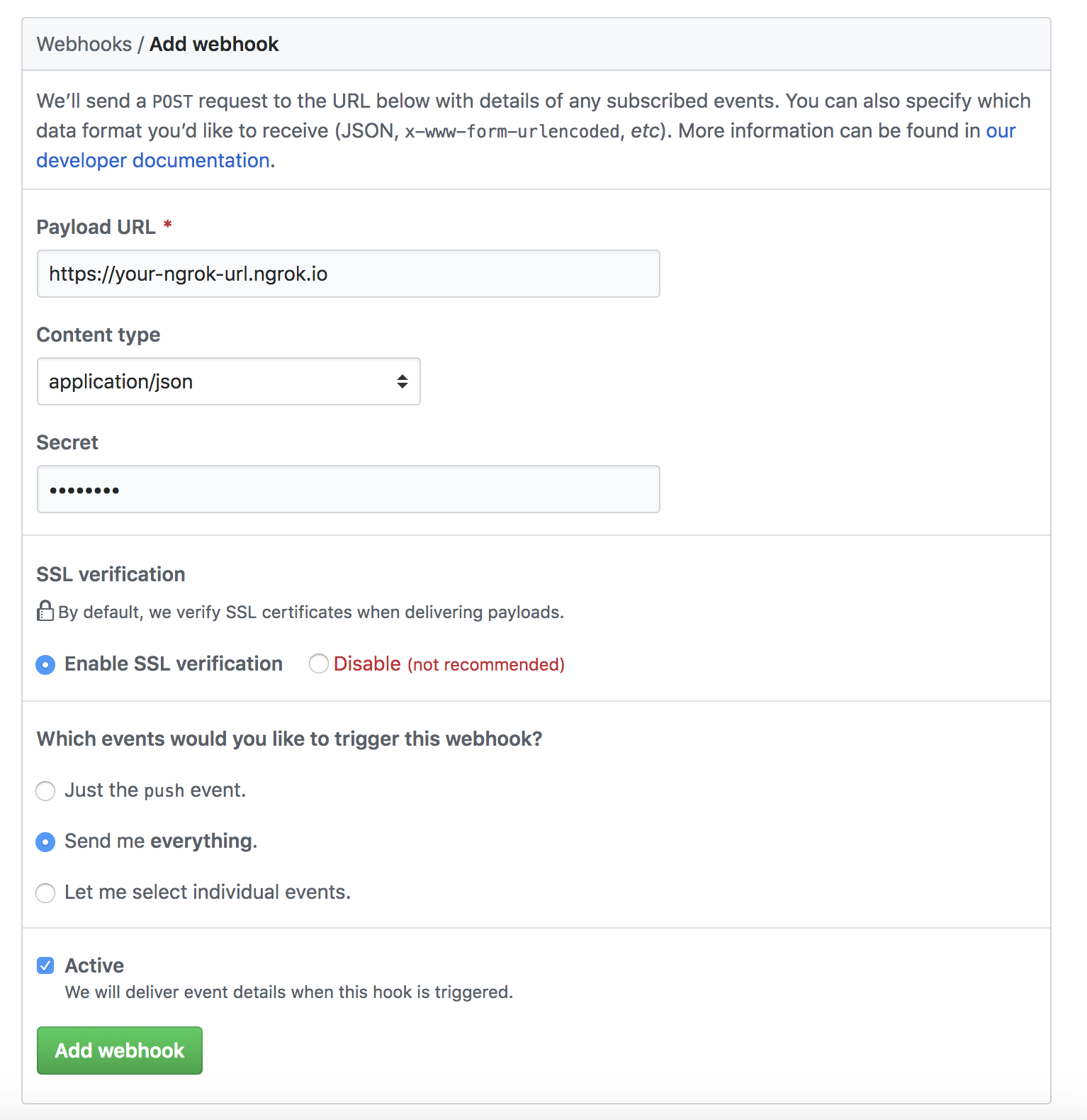
Then click Add webhook. Our new webhook should be good to go!
- Apply the url to webhook
- Add the secret
- Running an example